· 2 min read
Using ApplicationContext to Debug Spring Boot Faster
Using ApplicationContext directly can indeed be a handy approach for debugging without setting up the entire application infrastructure.
Often, we have multiple steps in reaching a piece of code to debug. For example, we’d set up infrastructure like doing an API call or setting up a database, Kafka, or something else.
A better way to debug is to create a unit test where you call your code with the same set of parameters you want to debug. Once your code is fixed, your test can stay for the future.
I usually keep a template for these regression bug kinds of tests.
For example, suppose I have an error in my MongoDB database. I know what database record causes the error. I can replicate this in the @DataMongoTest and validate it.
But assuming you have not written a unit test for debugging, there is another way to debug that doesn’t involve setting up the entire application infrastructure, and that’s to use ApplicationContext directly.
Using ApplicationContext, you can access any @Bean and call its method.
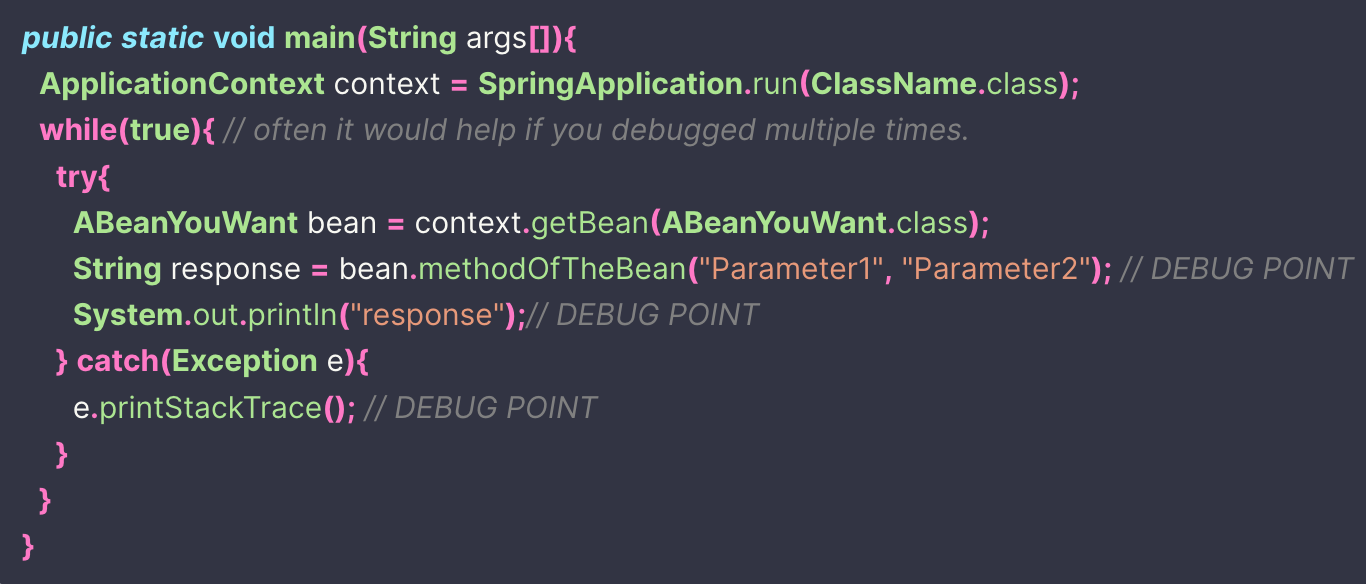
Here’s an example. (Don’t forget to put debug points)
public static void main(String args[]){
ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(ClassName.class);
while(true){ // often it would help if you debugged multiple times.
try{
ABeanYouWant bean = context.getBean(ABeanYouWant.class);
String response = bean.methodOfTheBean("Parameter1", "Parameter2"); // DEBUG POINT
System.out.println("response");// DEBUG POINT
} catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace(); // DEBUG POINT
}
}
}This was one of my favorite ways to debug before entering the world of Test Driven Development. Post TDD, my debugging has been even more easier and effective.