Ankush's Guide to
Test Driven Development
and Beyond
Approaching Test Driven Development To Become a 5x Developer
Statistics about the series
Welcome to Testing First Test Everything series!
In this series of articles, you’ll learn how you can increase your development skill by 5 times by learning something that ensures
- 1
You always produce logical bug-free code.
- 2
You produce extremely maintainable code.
- 3
You will code at a fast speed.
- 4
You produce automatic documentation for anyone else to read.
Introduction
Why?
I was a pretty good developer when I learned TDD, but after I spend around 2-3 months learning TDD, I saw that my coding skills became way too sharp. This series covers the philosophy of TDD along with practical examples.
How to Approach?
Try to practice the exercises in the language of your choice and upload them to GitHub 🙂. And if you want just share the link of your repo. I’d love to see it.
Free
The series of posts below is completely free 🆓. So, I’d really appreciate it if you share this with your friends via LinkedIn or Twitter, if you find value! This would help get more eyes on the series.
Share
If you have any questions reach out to me on LinkedIn. And I’ll respond. Your questions and feedback would make things better for everyone.
Getting Started
Understanding why you TDD and Testing are needed
TDD Level 1: Beginner
Learning the basics of TDD

Making TDD and Testing easier
Placeholder
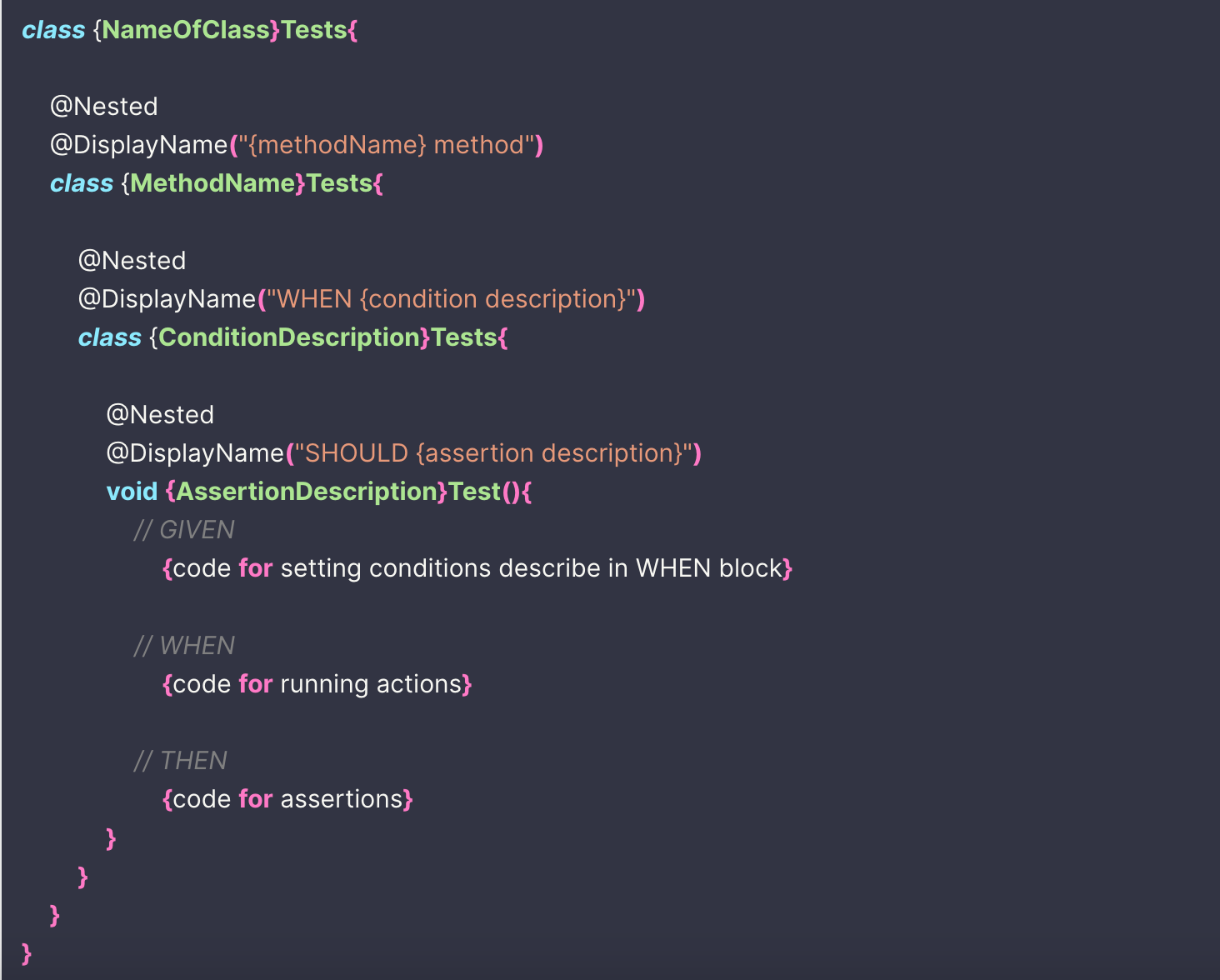
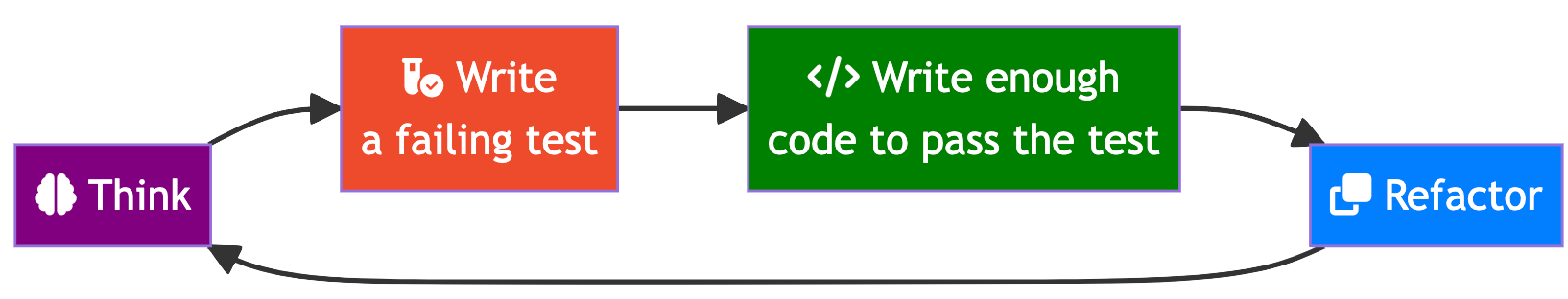
Thinking and writing cleaner tests with method/when/should blocks
A template for thinking and creating understandable uniform tests

TDD example on a backend - Upsert Method
Learn the foundation of TDD with a simple example explained in depth.
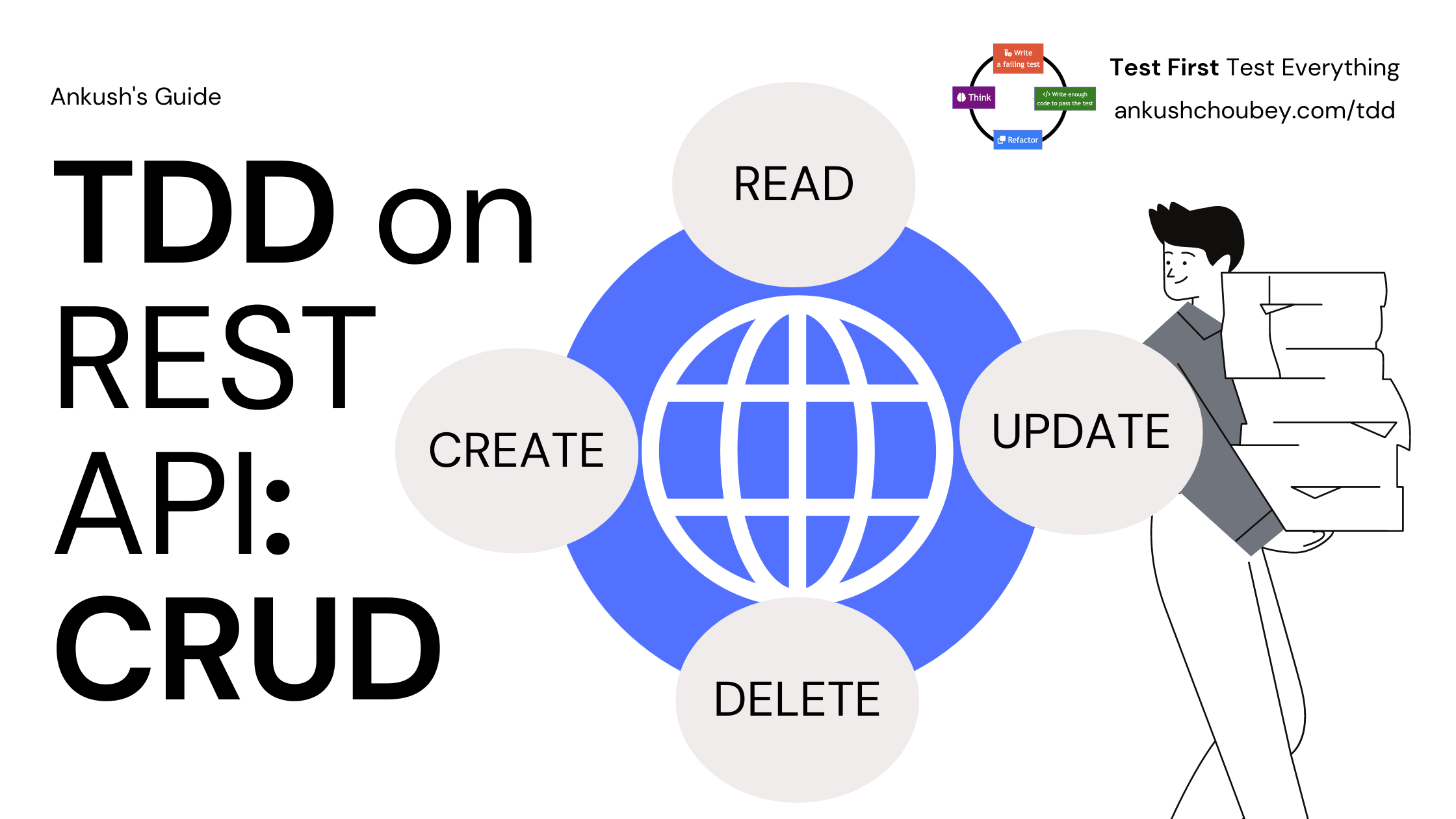
TDD example for REST API - CRUD
Extending our Movie example creating a REST API with TDD. Scenarios covered are Create, Read, Update and Delete.
TDD Level 1: Intermediate
Expanding our TDD scale by writing cleaner test and writing more tests
Pre-save Data Validation
Data validation at various stages minimizes bugs and unnecessary overhead, ensuring consistent and accurate information flow.
Avoid Mocks and understand the blurry lines between Unit and Integration Tests
The distinction between unit and integration tests blurs with embedded implementations, combining accuracy from both while overcoming limitations of traditional mocks and infra-heavy integration tests.
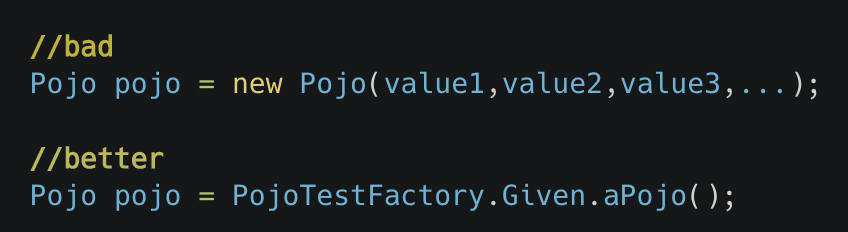
Writing cleaner tests with Test Data Factories
Consolidating object creation, mock of methods and more.
Writing cleaner tests with Fluent Assertions
Fluent Assertions make tests highly readable and English-like, presenting a concise structure that simplifies comprehension

TDD over JSON
TDD Example that saved around 2 hours
JUnit Template For Tracking Bugs in Unit Tests
Placeholder
TDD Level 2.5: UI
Making Testing on UI Easier
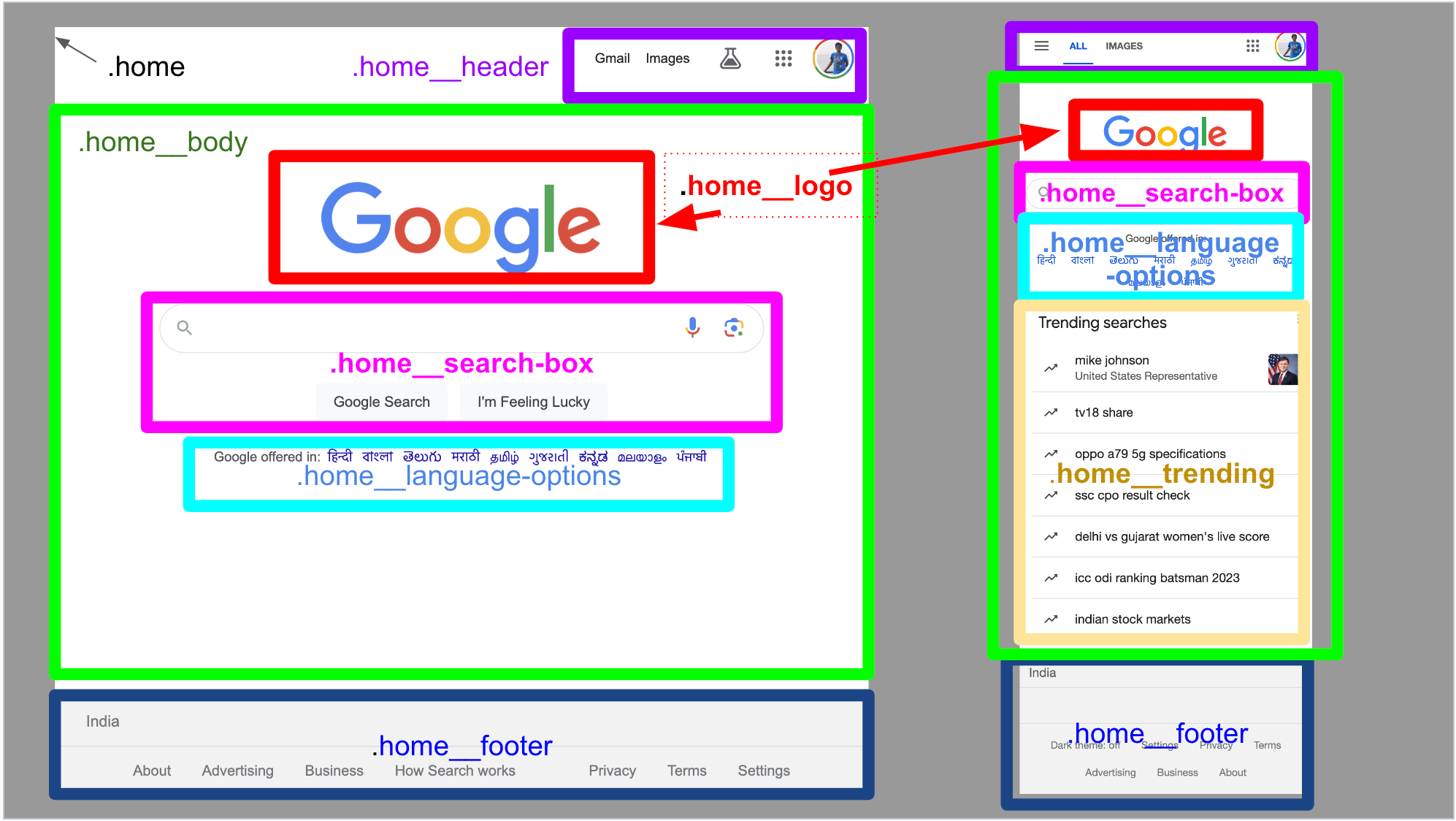
5 Step Process to Planning and Building a UI DOM Efficiently with Boxes, BEM and TDD
BEM, TDD, and thoughtful design supercharge web development by streamlining UI DOM planning for maximum efficiency.

Write Cleaner UI Tests with Page Object Model Pattern
Page Object Model can be used with any testing framework to write cleaner and simpler tests that are fast to write.
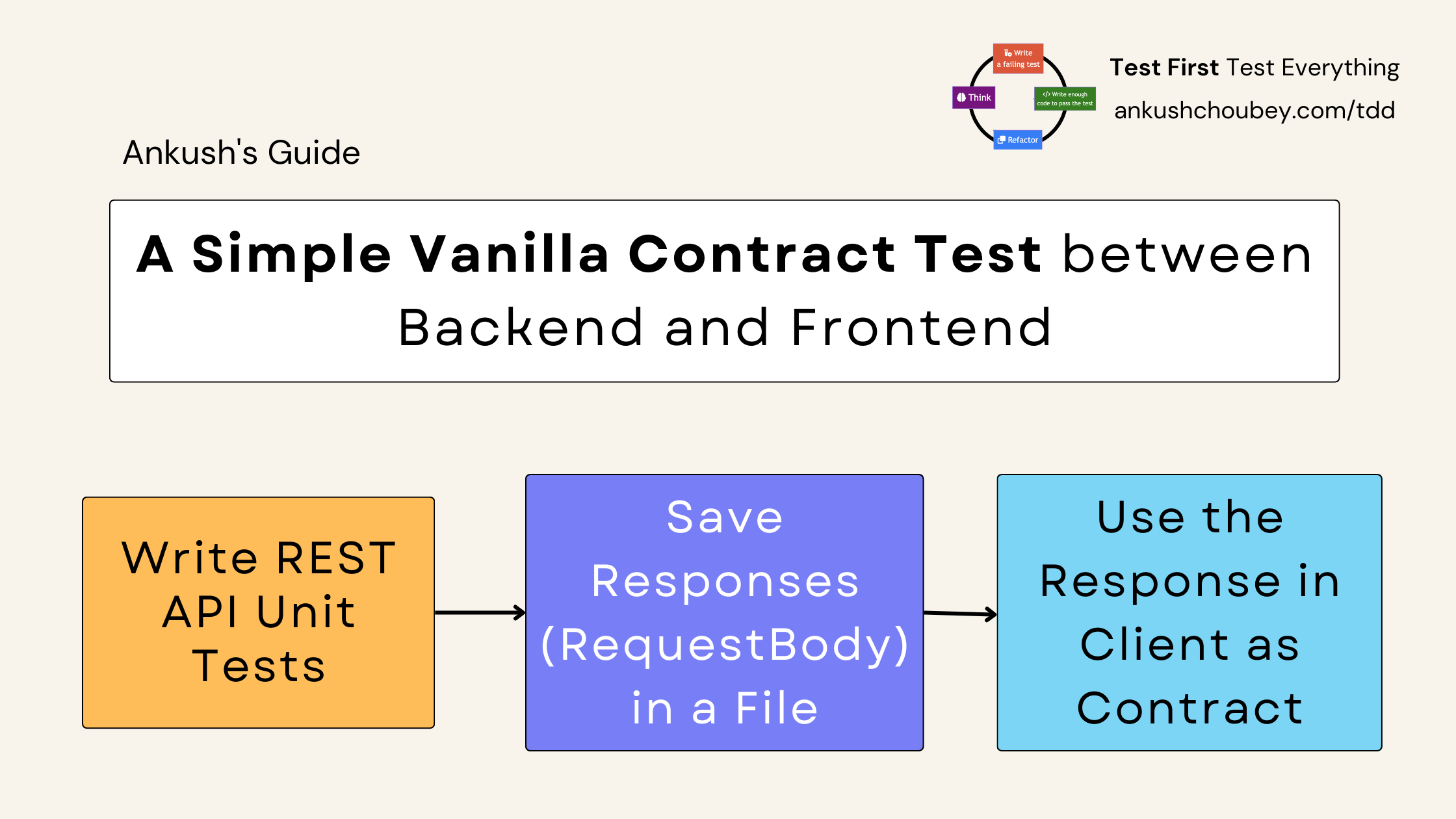
A Simple Vanilla Contract Test between Backend and Frontend
Response during unit tests can be saved in files which can be used for Testing UI.
TDD Level 3: TDD With time
How to continue with TDD practice with time
TDD Level 3: Red Flags and Tools 🚩
Tools
TDD Level 4: Testing Everything++
How to test everything and ensure the code is self sustainable and self-correcting

How to test interfaces, abstract classes and design patterns?
Testing interfaces, abstract classes, and design patterns efficiently can be tricky since parents and children depend on each other. We can write tests to eliminate these dependencies during the test time, making our tests very short and decoupled.
Automate Validation of Your Configuration
With TDD, you don't find any logical bugs. The remaining types of bugs are data bugs and configuration bugs. This article discusses configuration validations to find and fix config bugs.
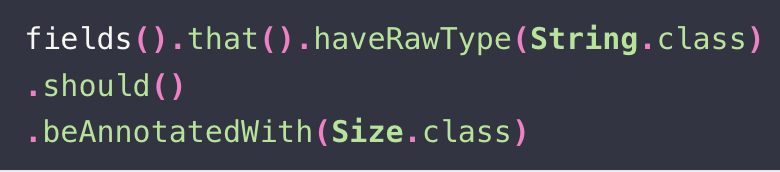
Enforcing Architecture with Architecture Testing
Architecture is a crucial pillar of accelerating product delivery. It's hard to keep a team in sync with architecture over time. Architectural testing can enforce architectural decisions as simple tests, dramatically reducing code review effort and extending code maintainability.
TDD Level 5: BDD
Behavior Driven Development

The Gist of Behavior Driven Development - BDD
The process that keeps everyone in sync
The need for executable specifications
Ideas shape development; specs sync teams; Gherkin tests ensure precision.
Writing better BDD specifications
Placeholder
You are really doing BDD when
Placeholder
BDD vs UI/UX/TDD - Understanding the Key Differences for Customer-Centric Problem Solving
BDD focuses on solving customer problems, not implementation details like UI. Those are addressed in other activities like wireframing and TDD.
Beyond TDD
Supporting factors

How to promote the habit of TDD within a Team
Promoting TDD within a team requires patience, consistent effort, and a focus on creating a positive and supportive environment for learning and improvement.
What to test to write after functional TDD
Placeholder

Ideal Development Workflow
From card picking to release
Mutation Testing
Placeholder
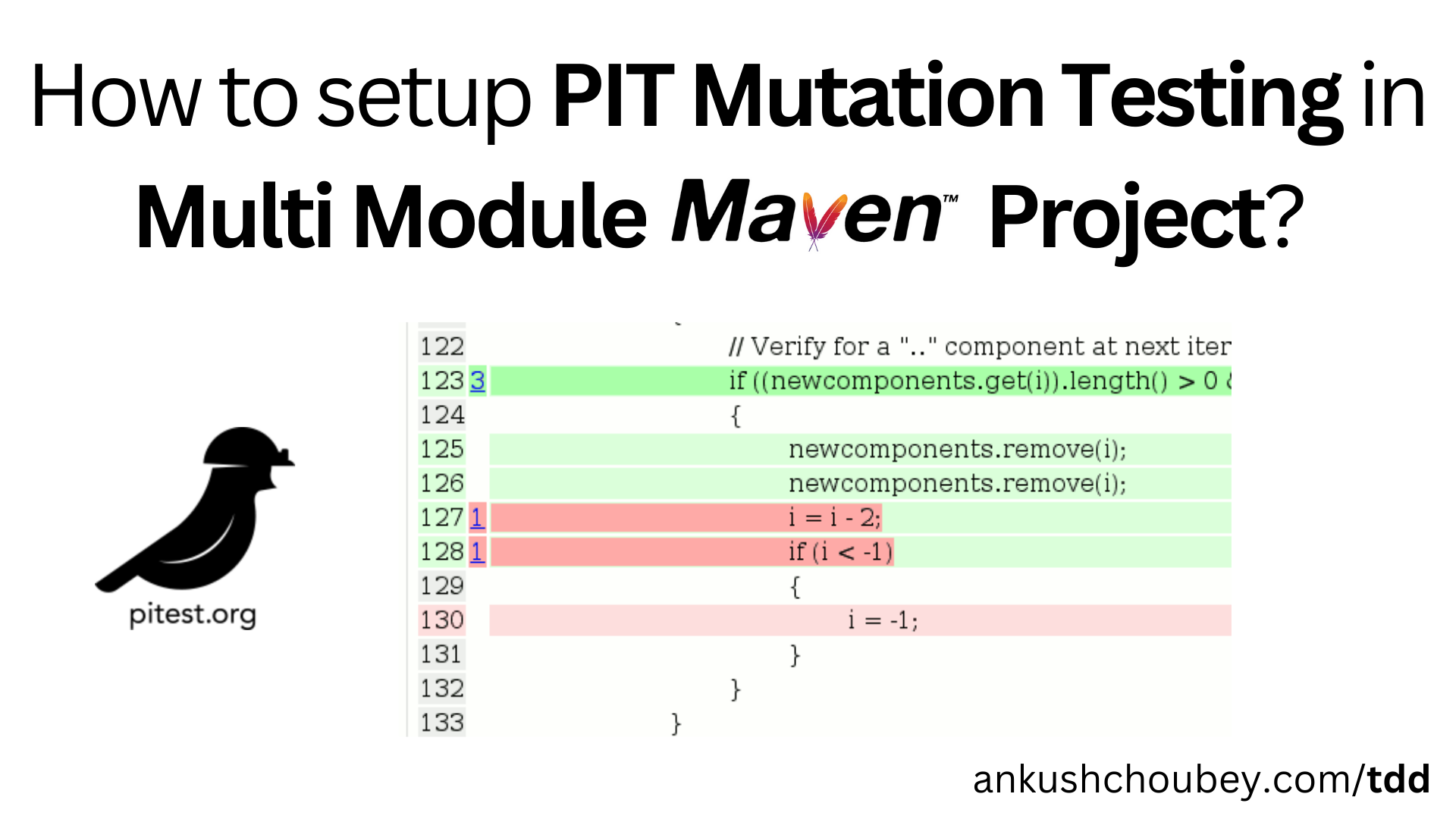
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up PIT Mutation Testing in a Multi-Module Maven Project
Boost your test quality with PIT Mutation Testing! Learn how to set up PIT in a multi-module Maven project to detect untested code paths and catch hidden bugs efficiently.

Chaos Engineering
A powerful way to increase resilence of a system

